Technological transformations open new opportunities and disrupt old patterns. Founded in 2006, Center on Global Transformation (CGT) provides a new framework for vanguard exploration of topics critical to analyzing and shaping the forces of economic change in a deeply interconnected, thoroughly dynamic world. CGT and its Pacific Leadership Fellows program focus on academic inquiry and policy analysis of international issues. CGT’s core mission is to: Foster and disseminate research that addresses global economic and technology transformation Develop and maintain a network…
SDG 9
Aspects of the prevailing global economic environment have not been conducive to rapid progress on Sustainable Development Goal 9. While financing for economic infrastructure has increased in developing countries and impressive progress has been made in mobile connectivity, countries that are lagging behind, such as least developed countries, face serious challenges in doubling the manufacturing industry’s share of GDP by 2030, and investment in scientific research and innovation remains below the global average.
Recent research at the School of Global Policy and Strategy
The mission of the UC San Diego Deep Decarbonization Initiative is to help guide a transition in the global economy toward net-zero carbon emissions. Our aim is to help real societies link the best science and technology with politically realistic economic strategies for putting new energy systems into place on the scale required to make a difference in global carbon emissions while meeting the energy needs of all of humanity. To accomplish this goal, we pursue research from the…
The Japan Forum for Innovation and Technology (JFIT) bridges Japan and San Diego by offering information and introductions to businesses and policymakers across the Pacific. As part of San Diego’s larger push to build stronger connections with Japan, UC San Diego’s School of Global Policy and Strategy has established JFIT as a hub for interaction, exchange and collaboration, through research projects, conferences, networking events and global education programs. JFIT also provides regular information and discussion groups on the UC…
The Regional Decarbonization Framework (RDF) anchors the San Diego region in emerging best practices from across the nation and globally. It charts science–based, feasible pathways toward expeditious deep decarbonization, proposing a paradigm shift in our local economy. The scale and pace of this effort will require partnerships between public and private sectors, particularly, business, labor and environmental communities. The input from these numerous stakeholders not only shaped the RDF itself, but initiated many of those collaborative efforts needed for…
In order to achieve zero carbon emissions, the US will need a plan. SDGPI is part of a coalition of the nation’s leading experts who have laid out the path forward to reach zero carbon emissions in the United States by 2050. Watch the Launch Read the Report Climate change represents a profound policy challenge to America and the world – requiring a response at a sweeping scale and with unprecedented speed centered on remaking the energy foundations of…
Gordon McCord
Gordon McCord along with other researchers from UCSD coauthored a study that shows intergenerational impacts of the BGD, showing that men who were in utero at the time were more likely to have a disability that affected their employment 15 years later, and had higher rates of cancer and lower educational attainment over 30 years later. Changes in the sex ratio among children born in 1985 suggest an effect of the BGD up to 100 km from the accident.
2023
Kyle Handley
Trade policy uncertainty (TPU) has become an important source of economic uncertainty and research. We review the main sources and measures of TPU. We then provide a conceptual framework for modeling TPU and methods of estimating and quantifying its effects. We analyze its role in trade agreements and discuss open questions for future research.
Francsico Garfias
Property titling enables tax collection and encourages private investment. Yet, governments across the developing world often fail to invest in land registration systems, such as cadastral maps, that record land ownership and values. In this paper, we describe and estimate the fiscal benefits and political costs that elected officials face when deciding whether to invest in this critical fiscal infrastructure. Focusing on Brazilian municipalities, we find that property tax revenue increases by over 10% following cadastre updates. Officials covet this revenue, but they simultaneously seek to secure their reelection, and investing in the cadastre can generate political costs by angering tax-averse voters or undermining clientelism. When these political costs are large, officials who do not face reelection pressures have
2021
David Victor and Gordon McCord
The Zero Carbon Action Plan (ZCAP) will serve as a roadmap for the U.S. based on the latest modeling, research and understanding of decarbonizing six key sectors (power, transport, industry, buildings, food and land use, and materials) supported by technical pathways to zero carbon by 2050, as well as supporting policy recommendations. The ZCAP was designed by a cohort of nearly 100 researchers and 19 Chairs who make up the Zero Carbon Consortium, who are experts in their fields of climate change policy; clean energy pathways modeling; industrial policy high-employment green economies; legislative and regulatory policy; electricity (power) generation; transportation; industry; buildings; sustainable land-use; and sustainable materials management.
Caroline Freund
Export superstars are important for export growth and diversification and are typically born large. Firm-level data on manufacturing trade from 32 developing countries show that the top five exporters account for on average nearly one-third of exports, 47 percent of export growth, and a third of the growth due to export diversification over a five-year period. Within countries and industries, export growth is positively correlated with the share of exports in the top five firms. Most of the top five exporters were already large five (or eight) years ago or are new firms; it is rare for these export superstars to emerge from the bottom half of the distribution of firm sizes. For countries where detailed data exist, superstars
John Ahlquist
This paper provides evidence that firms in Right-to-Work states tend to specialize in lower-quality products, making them more susceptible to competition with Chinese goods. However, while reducing unionization within manufacturing, import competition causes a robust increase in unionization outside of manufacturing, more than offsetting within-manufacturing declines.
2020
Teevrat Garg
There is a long-standing debate over whether new roads unavoidably lead to environmental damage, especially forest loss, but causal identification has been elusive. Using multiple causal identification strategies, we study the construction of new rural roads to over 100,000 villages and the upgrading of 10,000 kilometers of national highways in India. The new rural roads had precisely zero effect on local deforestation. In contrast, the highway upgrades caused substantial forest loss, which appears to be driven by increased timber demand along the transportation corridors. In terms of forests, last mile connectivity had a negligible environmental cost, while expansion of major corridors had important environmental impacts.
2020
Ulrike Schaede
San Diego’s innovation ecosystem offers new business opportunities for Japanese companies due to its close match to Japanese core industrial strengths, such as engineering, production technologies and infrastructure solutions. To be successful in San Diego, as compared to Silicon Valley, companies are advised to adopt a longer term investment horizon, an interest in future technologies that straddle existing industry borders, and the willingness to become an integral player in San Diego’s investment and startup community through immersion and inclusion.
2020
Joshua Graff Zivin
This paper examines the effect of stringent environmental regulations on firms’ environmental practices, economic performance, and environmental innovation. Reducing COD levels by 10% relative to 2005 levels is an aim of the Chinese 11th Five-Year Plan. We find that more stringent environmental regulations faced by firms are positively associated with a greater probability of reducing COD emissions; also, there exists an evident heterogeneous effect across industries with different pollution intensities. Stricter environmental regulations also account for the sharp decline in firms’ profits, capital, and labor. We find that firms rely more on recycling and abatement investment than on innovations when meeting environmental requirements.
2019
David Victor
Artificial intelligence helps make markets more efficient and easier for analysts and market participants to understand highly complex phenomena—from the behavior of electrical power grids to climate change. There is no reason to believe that these more efficient markets, on their own, will tackle the carbon problem. Instead, they will require overt policy signals.
2019
Krislert Samphantharak
This paper examines the extent to which a fiscal stimulus through car loans induces financial distress. Using data to study the impact of Thailand’s first-car-buyer tax rebate scheme at both individual and postcode levels, this paper finds that the program led to higher loan delinquency and crowded out other loan originations, which are symptoms implied by excessive debt burden..
Ruixue Jia
China is the world’s largest user of industrial robots. In 2016, sales of industrial robots in China reached 87,000 units, accounting for around 30 percent of the global market. To put this number in perspective, robot sales in all of Europe and the Americas in 2016 reached 97,300 units. Between 2005 and 2016, the operational stock of industrial robots in China increased at an annual average rate of 38 percent. In this paper, we describe the adoption of robots by China’s manufacturers using both aggregate industry-level and firm-level data, and we provide possible explanations from both the supply and demand sides for why robot use has risen so quickly in China.
Peter Cowhey
Everyone in Washington agrees on the need to promote “innovation” to ensure economic prosperity. However, high levels of unemployment have eroded confidence in the ability of our innovation system to create and maintain middle-class jobs for Americans. In our view, “innovation” can sustain employment and competitiveness, but only if we redefine our understanding of innovation and the policies supporting innovation.
David Victor
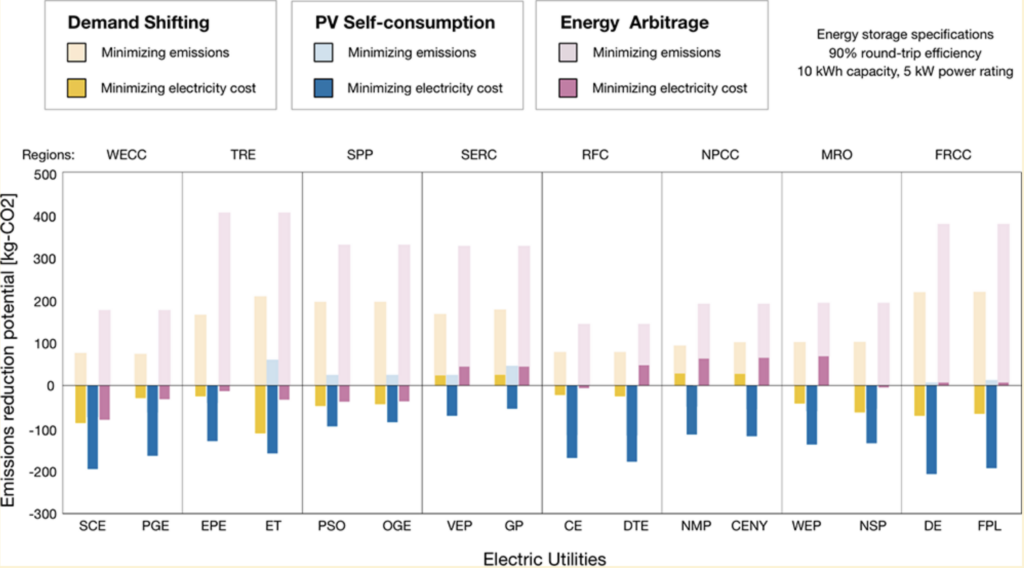
In many jurisdictions, policy-makers are seeking to decentralize the electric power system while also promoting deep reductions in the emission of greenhouse gases (GHG). We examine the potential roles for residential energy storage (RES), a technology thought to be at the epicenter of these twin revolutions. When operated with the goal of minimizing emissions, RES can reduce average household emissions by 2.2–6.4%. While RES is costly compared with many other emission-control measures, tariffs that internalize the social cost of carbon would reduce emissions by 0.1–5.9% relative to cost-minimizing operation. Policy-makers should be careful about assuming that decentralization will clean the electric power system, especially if it proceeds without carbon-mindful tariff reforms.
Richard Feinberg
This book examines the Cuban economy as it makes its early steps into developing a more dynamic market economy.
Barry Naughton
State enterprise reforms are underway in China, and include some positive and overdue corporate governance reform. However, the potential effectiveness of the reforms is compromised by the attempt of policy-makers to achieve three goals which form an “impossible trinity”: increase firm autonomy; improve oversight; and assign new developmental missions to state firms.