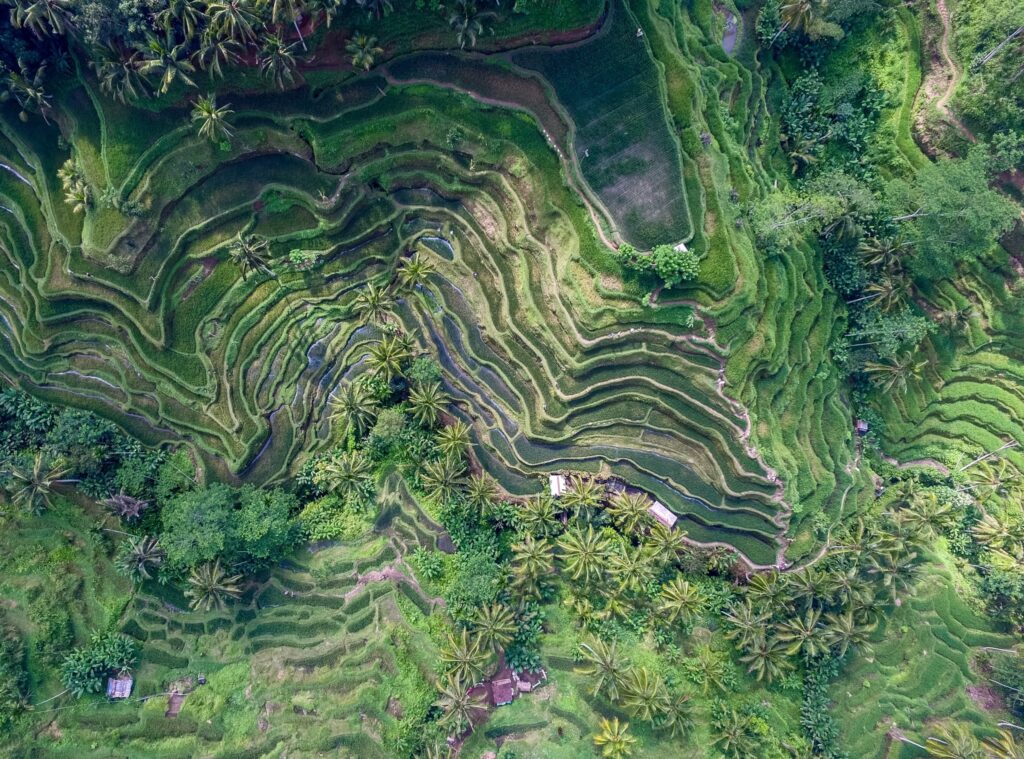
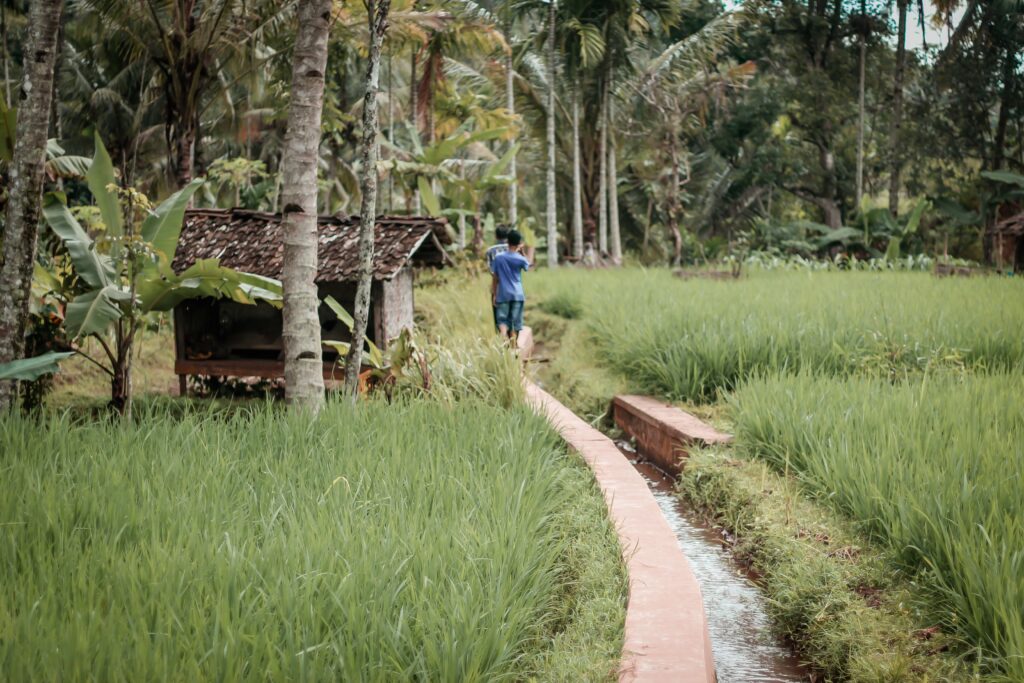
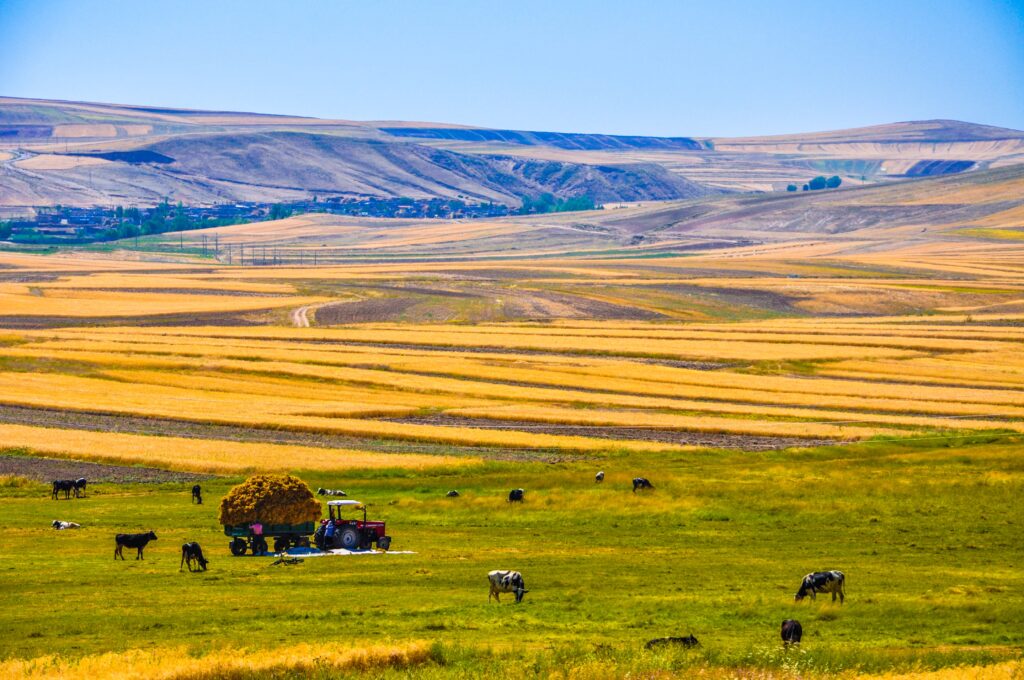
The Big Pixel Initiative is developing geospatial capacity to address our world’s greatest challenges at scale. Founded in partnership at UC San Diego’s Qualcomm Institute and School of Global Policy and Strategy, we have partnered with the DigitalGlobe Foundation to grow a living, learning laboratory related to everything spatial, to investigate and design best practices in geospatial data visualization, user experience interfaces, and design techniques for scientific discovery and decision-making. Resources The Big Pixel Team has partnered with the…
SDG 15
There are some encouraging global trends in protecting terrestrial ecosystems and biodiversity. Forest loss is slowing down, more key biodiversity areas are protected and more financial assistance is flowing towards biodiversity protection. Yet, the 2020 targets of Sustainable Development Goal 15 are unlikely to be met, land degradation continues, biodiversity loss is occurring at an alarming rate, and invasive species and the illicit poaching and trafficking of wildlife continue to thwart efforts to protect and restore vital ecosystems and species.
Recent research at the School of Global Policy and Strategy
Technological transformations open new opportunities and disrupt old patterns. Founded in 2006, Center on Global Transformation (CGT) provides a new framework for vanguard exploration of topics critical to analyzing and shaping the forces of economic change in a deeply interconnected, thoroughly dynamic world. CGT and its Pacific Leadership Fellows program focus on academic inquiry and policy analysis of international issues. CGT’s core mission is to: Foster and disseminate research that addresses global economic and technology transformation Develop and maintain a network…
Baja California SDG Monitoring Dashboard The dashboard translates the globally agreed Sustainable Development Goals into metrics that can guide decisions and progress of Baja California’s communities — Gordon McCord, Director, SDGPI Visit the dashboard → Project Overview The Baja California SDG Monitoring Dashboard is a joint initiative of the Secretaría de Economía e Innovación de Baja California (SEI‑BC) and the SDG Policy Initiative (SDGPI) at the UC San Diego School of Global Policy & Strategy. It localizes the United Nations 2030 Agenda by tracking Sustainable Development…
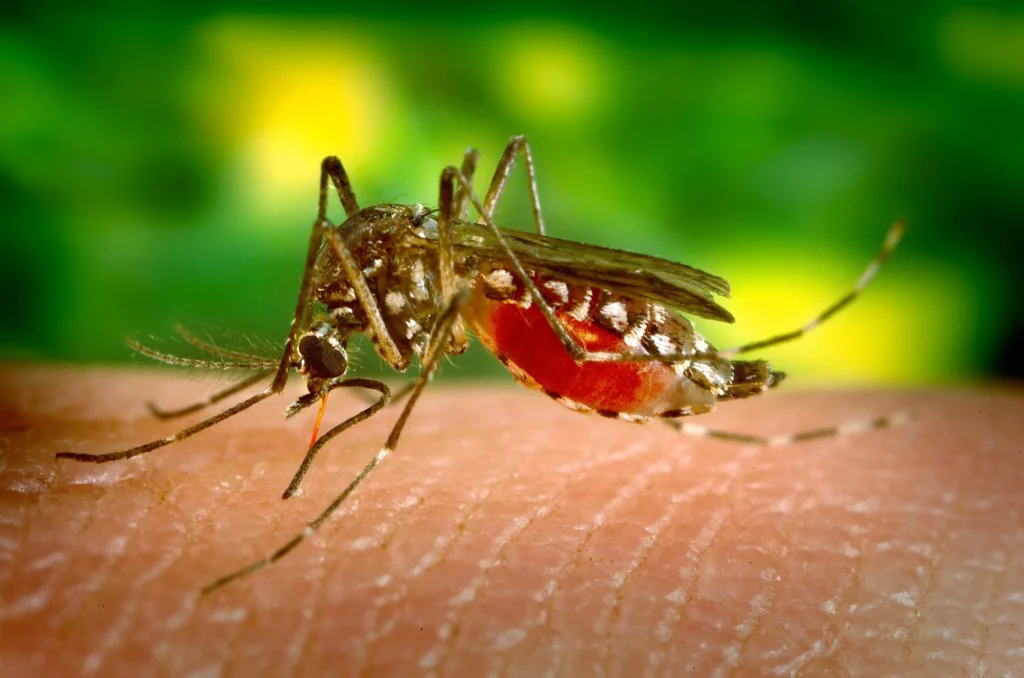
Project Overview With sponsorship from the Wellcome Trust and in collaboration with New Light Technologies Inc. and UNICEF, the SDG Policy Initiative is developing an online infectious disease prediction platform using real-time climate conditions to map predicted spikes in disease rates and to inform decision makers of public health resources required for disease prevention and treatment. The project will with dengue as a proof-of-concept, and then incorporate other diseases. Dengue fever is a climate-sensitive disease transmitted by the Aedes…
The FABLE Consortium has released its 2020 Report on Pathways to Sustainable Land-Use and Food Systems. Explore the latest trends in food and land-use with the new ‘Scenathon’ dashboard. Visit the FABLE Consortium Explore Scenathon Read Report Overview FABLE is a global consortium with teams of scientists in 20 countries modeling land use to 2050 in an integrated framework. Land use and land use change accounts for 23% of GHG emissions globally, biodiversity loss is accelerating at alarming rates, and…
Gordon McCord
Meeting ambitious climate targets will require deploying the full suite of mitigation options, including those that indirectly reduce greenhouse-gas (GHG) emissions. Healthy diets have sustainability co-benefits by directly reducing livestock emissions as well as indirectly reducing land use emissions. Increased crop productivity could indirectly avoid emissions by reducing cropland area. However, there is disagreement on the sustainability of proposed healthy U.S. diets and a lack of clarity on how long-term sustainability benefits may change in response to shifts in the livestock sector. Here, we explore the GHG emissions impacts of seven scenarios that vary U.S. crop yields and healthier diets in the U.S. and overseas. We also examine how impacts vary across assumptions of future ruminant livestock productivity and
Gordon McCord
Mexico aims to develop highly productive and sustainable food systems that ensure national self-sufficiency. This paper employs an integrated land-use modeling tool—the FABLE Calculator—to estimate the degree of policy ambition required for the country to meet mid-century climate, conservation and production goals in the land-use sector. We generate national-level land-use pathways to mid-century in terms of agricultural production, land use change dynamics, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and availability of land supporting biodiversity under varying assumptions of national policy and productivity changes. We estimate the effects of plausible efforts to achieve sustainability in land-use and food systems to 2050 against a business-as-usual benchmark. In the sustainable pathway, assumptions on agricultural land expansion, reforestation, and protected area expansion reflect existing and
Gordon McCord
There is an urgent need for countries to transition their national food and land-use systems toward food and nutritional security, climate stability, and environmental integrity. How can countries satisfy their demands while jointly delivering the required transformative change to achieve global sustainability targets? Here, we present a collaborative approach developed with the FABLE—Food, Agriculture, Biodiversity, Land, and Energy—Consortium to reconcile both global and national elements for developing national food and land-use system pathways. This approach includes three key features: (1) global targets, (2) country-driven multi-objective pathways, and (3) multiple iterations of pathway refinement informed by both national and international impacts. This approach strengthens policy coherence and highlights where greater national and international ambition is needed to achieve global goals
Teevrat Garg
Through a field experiment in Indonesia, we show that worker productivity was 8.22% lower in deforested relative to forested settings, where wet bulb globe temperatures were, on average, 2.84 °C higher in deforested settings. We demonstrate that productivity losses are driven by behavioral adaptations in the form of increased number of work breaks, and provide evidence that suggests breaks are in part driven by awareness of heat effects on work. Our results indicate that the cooling services from forests have the potential for increasing resilience and adaptive capacity to local warming.
Jennifer Burney
Historically, human uses of land have transformed and fragmented ecosystems, degraded biodiversity, disrupted carbon and nitrogen cycles, and added prodigious quantities of greenhouse gases (GHGs) to the atmosphere. However, in contrast to fossil-fuel carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, trends and drivers of GHG emissions from land management and land-use change (together referred to as ‘land-use emissions’) have not been as comprehensively and systematically assessed. Even where land-use change emissions are negligible or negative, total per capita CO2-equivalent land-use emissions remain near 0.5 tonnes per capita, suggesting the current frontier of mitigation efforts. Our results are consistent with existing knowledge—for example, on the role of population and economic growth and dietary choice—but provide additional insight into regional and sectoral trends.
2021
Teevrat Garg
There is a long-standing debate over whether new roads unavoidably lead to environmental damage, especially forest loss, but causal identification has been elusive. Using multiple causal identification strategies, we study the construction of new rural roads to over 100,000 villages and the upgrading of 10,000 kilometers of national highways in India. The new rural roads had precisely zero effect on local deforestation. In contrast, the highway upgrades caused substantial forest loss, which appears to be driven by increased timber demand along the transportation corridors. In terms of forests, last mile connectivity had a negligible environmental cost, while expansion of major corridors had important environmental impacts.
2020
Teevrat Garg
This paper documents the effect of primary forest cover loss on increased incidence of malaria. Back of the envelope calculations indicate that the morbidity-related malaria-reducing local benefits of primary forests are at least $1-$2 per hectare.
Jennifer Burney
Techno–ecological synergy is a framework for engineering mutually beneficial relationships between technological and ecological systems, as an approach to augment the sustainability of solar energy across a diverse suite of recipient environments, including land, food, water, and built-up systems.
David Victor
One of the most significant impacts of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) has been the establishment of a participatory process for Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD+). We analyse the case of Brazil, the country whose land-use emissions from deforestation and forest degradation have declined the most. Through semi-structured interviews with 29 country policy experts – analysed in full text around 7 categories of activities that existing literature identifies as central elements of an effective governance system – we find weak links between the international REDD+ system and what actually happens on the ground inside Brazil.
2019
Peter Cowhey
Many researchers around the world are working to apply gene editing technologies with the hope of safely and effectively engineering populations of insects and other pest arthropods in the wild either to reduce diseases, such as malaria or dengue fever, or to control agricultural pests, such as those that transmit the bacterium that causes citrus greening disease. Important benefits could be realized if these research efforts are successful, but realizing these benefits requires sustained, open, and inclusive attention to potential environmental and social impacts and regulatory and implementation challenges.